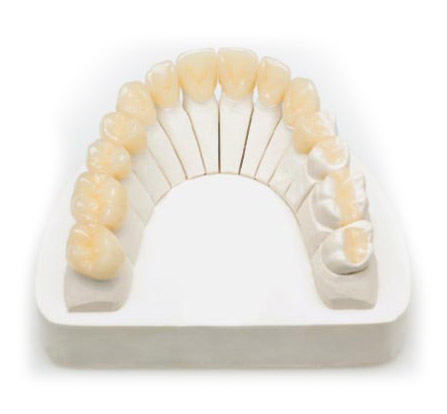
Why Zirconia Crowns?
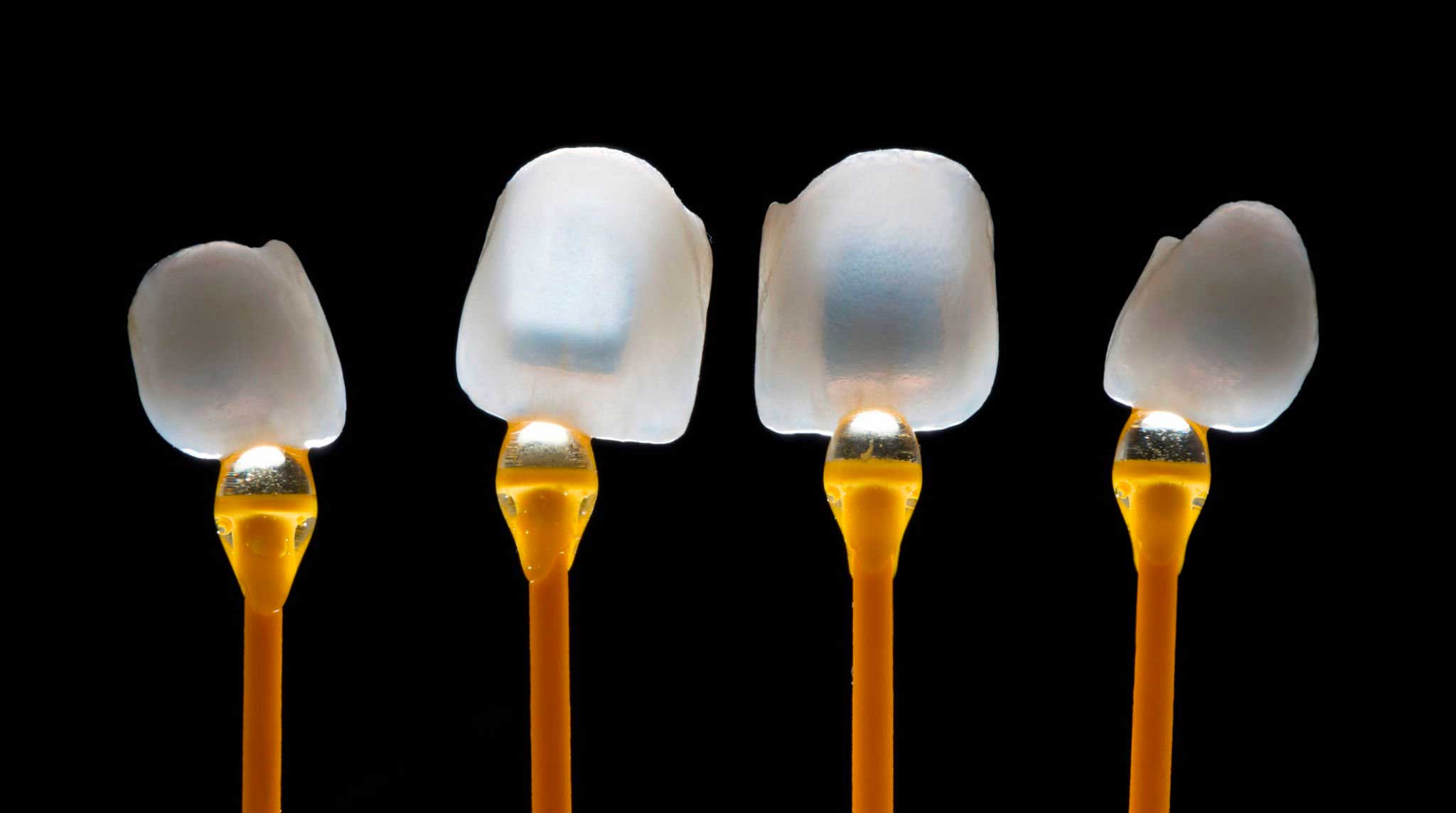
A zirconia crown is made from an incredibly hard ceramic material that is practically indestructible. Because of this feature, zirconia is especially suited for posterior crowns and multi-unit bridges. Do you have patients in your practice that seem to wear out every restorative material known to man? Zirconia’s durability is especially suited for patients with bruxism or a hard bite.
USA-Made Crowns From a Reliable, High-Quality Zirconia Dental Lab
No matter the situation, Stomadent Dental Laboratory is the best zirconia dental lab that can provide you with a zirconia restorative solution appropriate for your restorative application. Partner with us for fast, reliable, high-quality dental lab services.
Types of Zirconia Crowns
Stomadent Dental Laboratory is proud to offer the dentist three distinct types of zirconia crowns: full-contour zirconia, full-contour all-translucent zirconia, and porcelain-fused-to-zirconia.
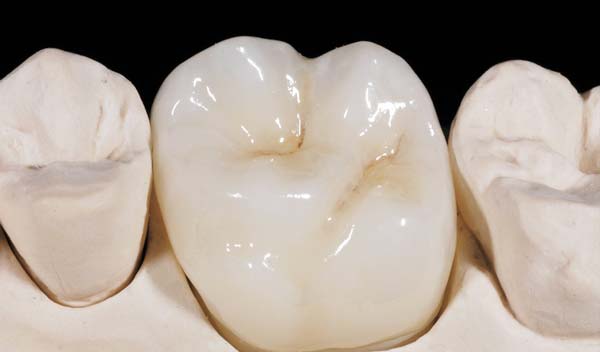
full contour
Full-contour zirconia is known for its superior strength and is best suited for patients with a heavy bite, bruxism, or even heavy canine guidance.
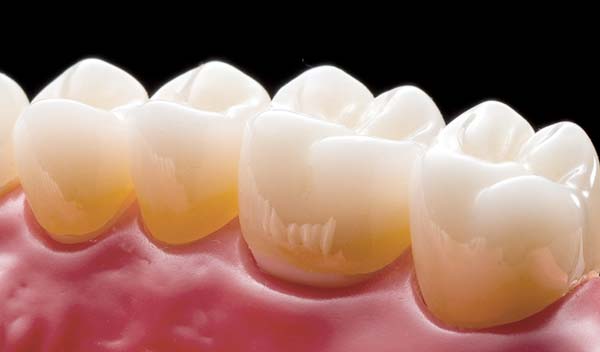
full contour all-translucent
A full-contour translucent zirconia crown is more suited for areas that need to be visually pleasing yet are subjected to far less biting and grinding forces.
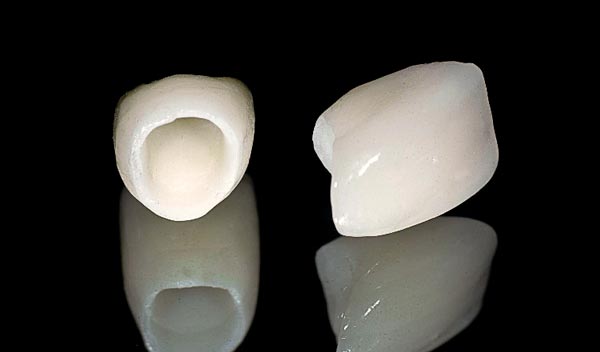
Porcelain-fused-to-Zirconia
Porcelain fused-to-zirconia (PFZ) involves fabricating a full-contour zirconia crown. A window on the face of the crown is cut out so as not to compromise the strength of the zirconia. Then, an overlay of translucent porcelains are layered and baked on. External stains are applied for characterization with incredible results! PFZ is the ultimate combination of both resistance to wear and aesthetics.
Special Features of Zirconia
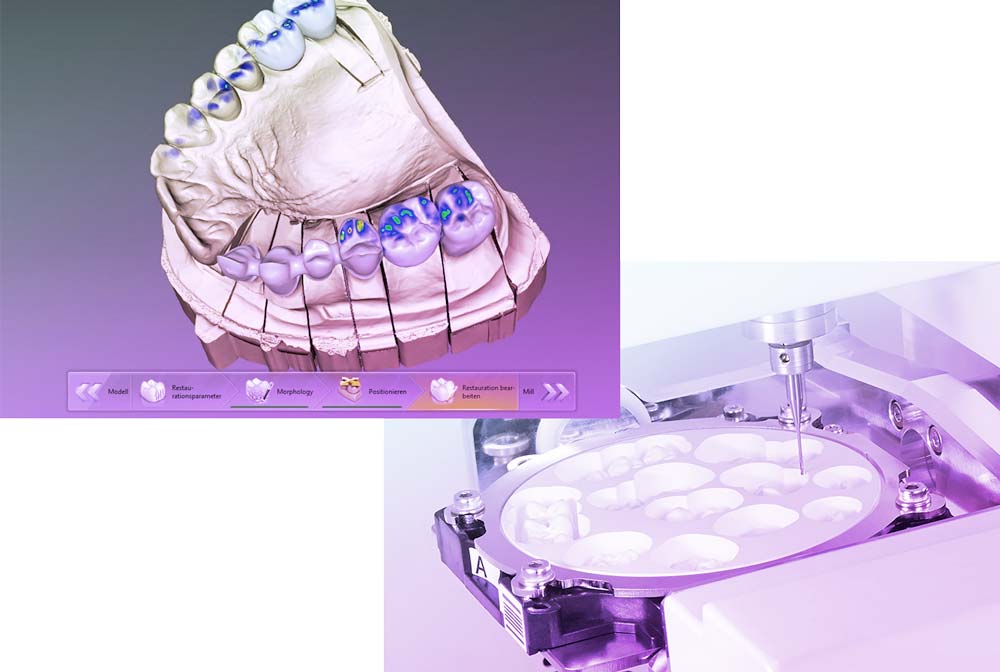
Zirconia crowns were first introduced to dentistry in 2010. Before being milled into crowns, zirconia was used in dentistry for endodontic posts and dental implants. The bulk material is provided to the dental laboratory in the form of pressed solid blocks. These blocks are then milled into a 3D crown or framework using CAD/CAM production, assuring a void-free, precise-fitting restoration every time.
There are no metals involved in the process, which allows for aesthetically pleasing crown margins with no visible dark lines or shadows.
Restorative Uses of Zirconia
Zirconia has a variety of restorative uses, including full-crown coverage, multi-unit bridges, frameworks for porcelain-fused-to-zirconia crowns and bridges, and even veneers.
MATERIAL PROPERTIES:
What Is Zirconia Made Of?
Zirconia restorations are made from zirconium dioxide, a metal oxide. The incredible strength of monolithic zirconia used for dental restorations comes from its tetragonal crystalline properties. The all-ceramic material doesn’t require any unsightly metal substructure for stability, is resistant to wear, and difficult to crack.

Tooth Preparation Guidelines for Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns require a mechanically-retentive tooth preparation similar to that used for porcelain-fused-to-metal crowns. Sharp angles and edges must be rounded, and shoulders should be chamfered. Gingival margins are a minimum of 0.6 mm in depth. Axial walls have a minimum of 1.0 mm depth with an anatomical occlusal reduction of 1.5 mm. If this seems aggressive, it is compared to the preparation guidelines for other types of all-ceramic dental restorations (i.e. e.Max).
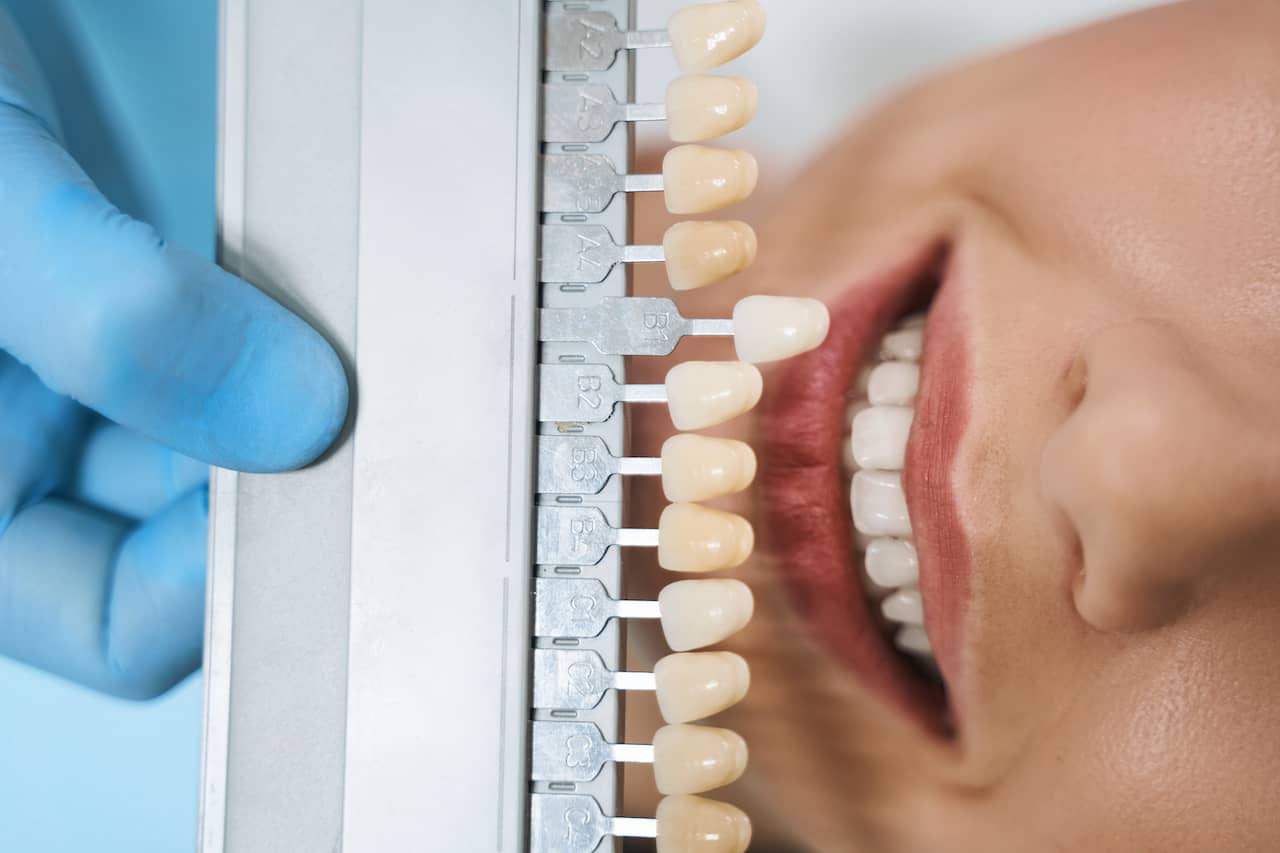
Color Choices
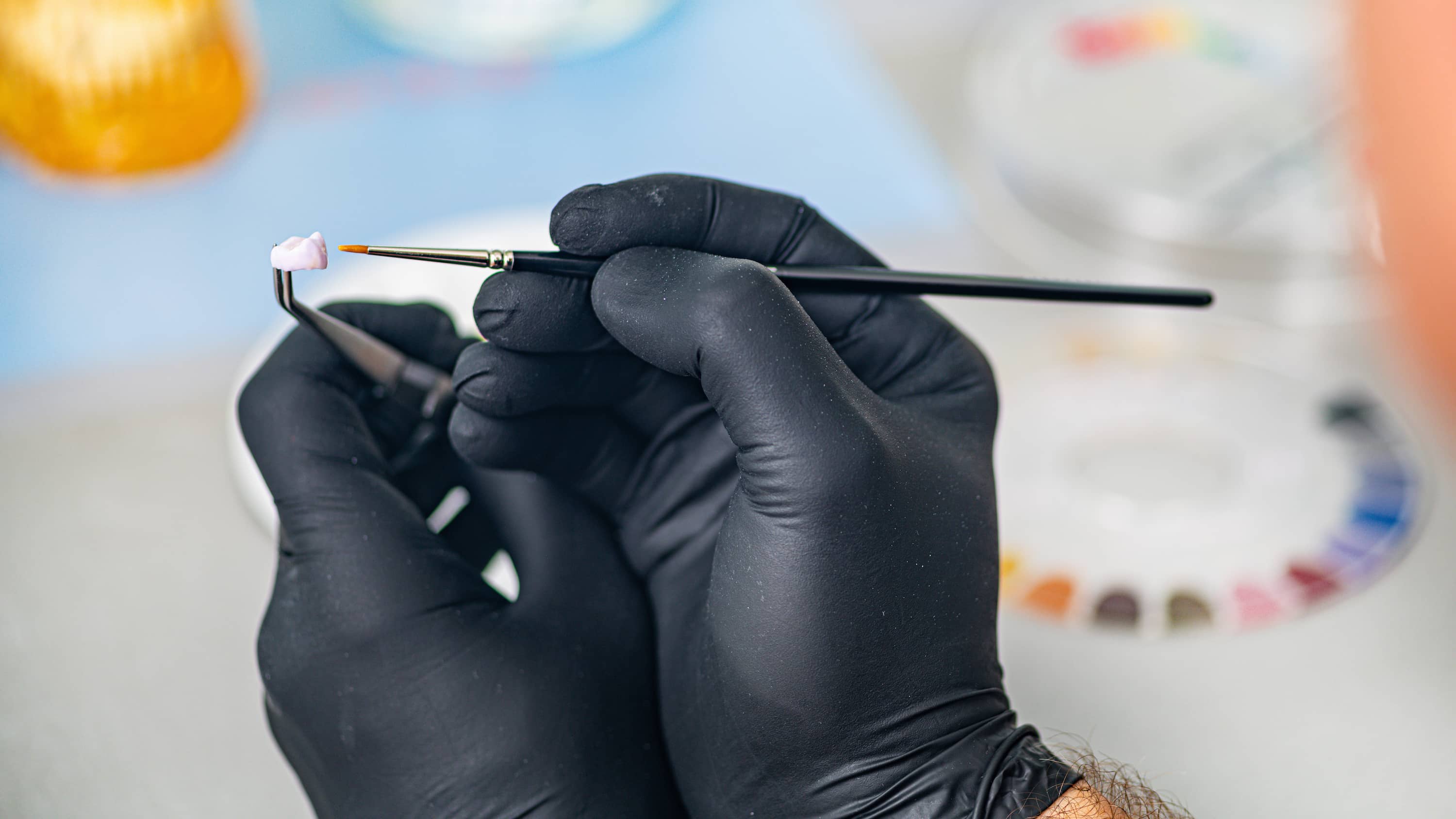
Our zirconia dental lab offers multiple color options that correspond to the Vita Classic Shade Guide. Bleaching shades are also available. Custom staining allows the finished zirconia restoration to blend seamlessly with existing restorations and natural teeth.
Delivery and Cementation
Minor adjustments may be made at chairside using a combination of green stones or diamond burs.
Cementation is achieved via mechanical retention using a glass ionomer resin dental cement.
How Long Do Zirconia Crowns Last?
The average lifespan of zirconia crowns is currently unknown. Zirconia crowns are relatively new to dentistry as compared to other types of crowns. Therefore, longevity studies are currently unavailable. The average lifespan is estimated to be approximately 20 years. Of course, how long any dental restoration lasts in vivo depends heavily upon the home care and habits of the individual patient.
Are Zirconia Crowns Safe?
All-ceramic zirconia dioxide has been used extensively in the field of medical prosthetics, such as joint replacements, since the 1960s. In the 1990s, zirconia was introduced to dentistry in the form of endodontic posts and dental implants. Milled zirconia crowns became commercially available in 2010. Zirconia has a long history of use in the human body. Its strength and biocompatibility make it the ideal, safe choice for a restorative dental material. Many patients are concerned about the use of metals in dental restorations and how they may lead to adverse health effects. With zirconia, this concern is alleviated because the material is chemically unreactive.

Zirconia: The Pros and Cons
Consider the Advantages…
Since zirconia possesses incredible strength, bridge frameworks are milled from a solid block of monolithic zirconia, there is no need for an underlying metal framework or substructure for support that may show through the final restoration. Even with recession, there are no visible dark lines around crown margins.
…and Disadvantages of the Zirconia Crown Material
Milled monolithic zirconia is a fairly opaque material. This is an aesthetic problem. While it hides tooth discoloration and large core build-ups well, it lacks the translucent and refractory properties that make it appear natural and lifelike. Manufacturers have developed a translucent version of zirconia that is custom stained and sintered (baked) at high temperatures onto the monolithic zirconia layer in order to allow esthetic crowns to be produced. Once processed, this translucent version closely mimics the translucence of natural teeth at the slight expense of the material’s strength.
The biggest disadvantage of zirconia crowns resides in their strength — ironically, the best feature. Should it ever become necessary to create an endodontic access or to cut the crown off, it will be a difficult process.
Taking Impressions in order of preference
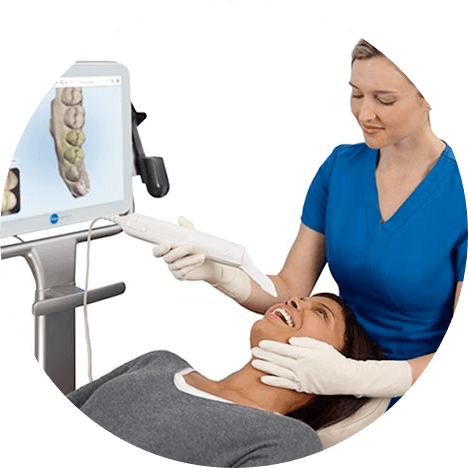
Impression-free scans for a complete digital workflow
The crown preparation, hard tissue, and surrounding soft tissue are scanned at chairside and transferred to the dental lab electronically for integration into the digital workflow of the laboratory.
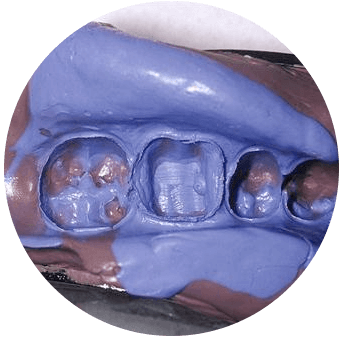
1. Hybrid impressions
Utilizing scannable impression material and impression trays, the impressions and bite registrations are individually scanned into STL files. Images are created and used to print 3D models in the dental lab. These models are then carried through digital processing.
2. Traditional impressions
Polyvinyl siloxane impressions and bite registrations are sent to the laboratory for scanning and are digitized into the workflow for CAD/CAM processing.
ranging from $103 to $160 per unit
What Is the Average Laboratory Cost of a Zirconia Crown?
Stomadent Dental Lab offers different three types of Zirconia crowns with competitive price points ranging from $103 to $160 per unit. Additional services to customize crowns, such as fitting the crown to an existing removable partial denture or a metal lingual surface, will incur additional fees. Please see our Fee Schedule for a complete description of our pricing.
Certification
Stomadent Dental Laboratory is a Zirconia certified provider. The staff at our Zirconia dental lab undergoes extensive training and on-going continuing education from our supplier to stay abreast of the latest advances in the manufacture and processing of all of our Zirconia restorations.
Partner with us. We will offer an incredible solution for your patient’s unique needs at a price point that won’t break the bank!